Strength of Material Sheet 17
-
1) Question.
Laminated springs are subjected to
Answer. -
2) Question.
A laminated spring is supported at
Answer. -
3) Question.
A laminated spring is given an initial curvature because
Answer. -
4) Question.
A simply supported beam with rectangular cross-section is subjected to a central concentrated load. If the width and depth of the beam are doubled, then the deflection at the centre of the beam will be reduced to
Answer. -
5) Question.
If the length of a simply supported beam carrying a concentrated load at the centre is doubled, the deflection at the centre will become
Answer. -
6) Question.
A cantilever beam carries a uniformly distributed load from fixed end to the centre of the beam in the first case and a uniformly distributed load of same intensity from centre of the beam to the free end in the second case. The ratio of deflections in the two cases is
Answer. -
7) Question.
A simply supported beam of circular cross-section with diameter d and length 1 carries a concentrated load W at the centre of the beam, The strength of the beam is proportional to
Answer. -
8) Question.
If the deflection at the free end of a uniformly loaded cantilever beam of length 1m is equal to 7.5 mm, then the slope at the free end is
Answer. -
9) Question.
A simply supported beam ABC of length 1 carries a concentrated load P at an intermediate point B. If the slope at A is 0.75 times the slope at C, then the length of portion AB is equal to
Answer. -
10) Question.
If the deflection at the free end of a uniformly loaded cantilever beam is 15mm and the slope of the deflection curve at the free end is 0.02 radian, then the length of the beam is
Answer. -
11) Question.
Slope at the end of a simply supported beam of a span l with uniformly distributed load w/unit length over the entire span is given by
Answer.Where EI is flexural rigidity of the beam.
-
12) Question.
A beam ABC rests on simple supports at A and B with BC as an overhang. D is centre of span AB. If in the first case a concentrated load P acts at C while in the second case load P acts at D, then the
Answer. -
13) Question.
A beam of overall length 1 rests on two simple supports with equal overhangs on both sides. Two equal loads act at the free ends. If the deflection at the centre of the beam is the same as at either end, then the length of either overhang is
Answer. -
14) Question.
The portion, which should be removed from top and bottom of a circular cross-section of diameter d in order to obtain maximum section modulus, is
Answer. -
15) Question.
Two beams, one of circular cross-section and other of square cross-section, have equal areas of cross-section. If subjected to bending
Answer. -
16) Question.
For no torsion, the plane of bending should
Answer. -
17) Question.
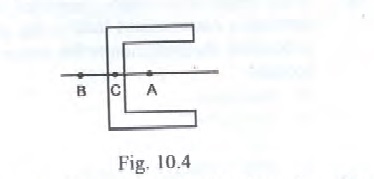 The shear centre in the channel section shown in Fig. 10.4 will be at Answer.
The shear centre in the channel section shown in Fig. 10.4 will be at Answer. -
18) Question.
A beam of uniform strength has at very cross-section same
Answer. -
19) Question.
A beam of I-section 600 mm deep and 200 mm wide has flanges 25 mm thick and web 20 mm thick. If the shear stress in the web at the junction of flange and web is q, then the shear stress in the flange at the junction is
Answer. -
20) Question.
A beam of triangular cross section is placed with its base horizontal. The maximum shear stress intensity in the section will be
Answer.

