Strength of Material Sheet 16
-
1) Question.
A prismatic bar when subjected to pure bending assumes the shapes of
Answer. -
2) Question.
A beam of square cross-section with side 100 mm is placed with one diagonal vertical. If the shear force acting on the section is 10 kN, the maximum shear stress is
Answer. -
3) Question.
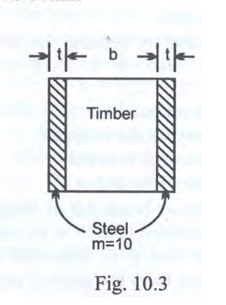 If the maximum flexural stress in timber joist of the flitched beam shown in Fig.10.3 is 7 N/mm², then the maximum stress reached in steel is Answer.
If the maximum flexural stress in timber joist of the flitched beam shown in Fig.10.3 is 7 N/mm², then the maximum stress reached in steel is Answer. -
4) Question.
A beam of rectangular cross-section is 100 mm wide and 200 mm deep. If the section is subjected to a shear force of 20 kN, then the maximum shear stress in the section is
Answer. -
5) Question.
Maximum shear stress in a circular cross-section is
Answer.Where is average shear stress
-
6) Question.
A flitched beam consists of a wooden joist 150 mm wide and 300 mm deep strengthened by steel plates 10 mm thick and 300 mm deep one on either side of the joist. If modulus of elasticity of steel is 20 times that of wood, then the width of equivalent wooden section will be
Answer. -
7) Question.
Of the two prismatic beams of same material, length and flexural strength, one is circular and other is square in cross-section. The ratio of weights of circular and square beams is
Answer. -
8) Question.
Of the several prismatic beams of equal lengths, the strongest in flexure is the one having maximum
Answer. -
9) Question.
The ratio of width to depth of a strongest beam that can be cut out of a cylindrical log of wood is
Answer. -
10) Question.
A portion of a beam between two sections is said to be in pure bending when there is
Answer. -
11) Question.
If a cantilever beam carries a uniformly distributed load over its entire length, then shapes of shear-force diagram and bending-moment diagram respectively are
Answer. -
12) Question.
A simply supported beam of length 1 carries a load varying uniformly from zero at left end to maximum at right end. The maximum bending moment occurs at a distance of
Answer. -
13) Question.
A prismatic beam of length I and fixed at both ends carries a uniformly distributed load. The distance of points of contraflexure from either end is
Answer. -
14) Question.
A beam of overall length I with equal overhangs on both sides carries a uniformly distributed load over the entire length. To have numerically equal bending moments at centre of the beam and at supports, the distance between the supports should be
Answer. -
15) Question.
The relationship between the radius of curvature R, bending moment M and flexural rigidity EI is given by
Answer. -
16) Question.
A prismatic beam fixed at both ends carries a uniformly distributed laod. The ratio of bending moment at the supports to the bending moment at mid-span is
Answer. -
17) Question.
A cantilever beam AB of length L carries a concentrated load W at its midspan C. If the free end B is supported on a rigid prop, then there is a point of contraflexure
Answer. -
18) Question.
The maximum bending moment due to a moving load on a fixed ended beam occurs
Answer. -
19) Question.
The variation of the bending moment in the portion of a beam carrying linearly varying load is
Answer. -
20) Question.
According to Rankine's hypothesis, the criterion of failure of a brittle material is
Answer.

